Image stacking is a technique that is primarily used for improving
astronomical images.
When you try to photograph a planet such as Jupiter through a telescope, the
Earth's atmosphere continuously distorts the image so that the images usually
look pretty blurry, they dance around a lot and they contain a lot of noise.
However, by taking several hundred images, "registering" (aligning their
centers) then "stacking" them (adding them all together pixel-by-pixel then
dividing each pixel by the number of images) the blurriness diminishes and
amazing detail often emerges. (You might also want to consider using the
freeware program RegiStax which is a truly excellent image stacking program.)
The Stack Images control window:
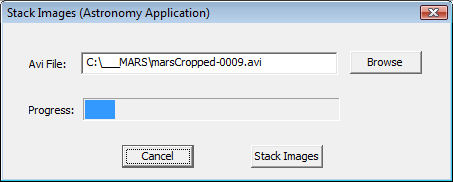
Browse: Brings up a file selector window. Select an AVI file containing
the images you want to stack. In the above example, the marsCropped-0009.avi
file was captured using the "Create an astronomy Video" capture mode.
Progress: If the image stacking process is underway, the progress bar
will proceed from left to right indicating the progress of the stacking
algorithm. You can see in the above example that image stacking is about 1/10th
finished.
Stack Images: Begin the image stacking operation. Stacking can be aborted
using the Escape key or the Cancel button.
Cancel: If image stacking was NOT underway, this causes the "Stack
Images" window to close. If image stacking IS underway, a message box pops up
asking "Would you like to abort image stacking?". If you answer yes, the frames
that have already been processed will be averaged and displayed in a Stacked
Image Window.
Stacked Image window: After stacking has completed (either by normal
completion or by Cancel or Escape key) a "Stacked Image Window will be displayed
showing the result of the image stacking operation:
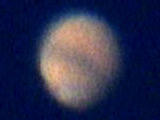
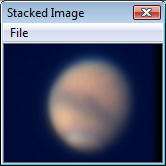
One original image Stacked
image
The stacked image window has a File menu item that will let you save the stacked
image as a JPG file or a BMP file: